Constraints in Primavera P6 Schedules
Ideally in projects, the natural flow of time through the project using durations and logic should be respected. However, sometimes there are date restrictions that cannot be built into network logic. Constraints provide additional control over start and finish dates when specific deadlines or project conditions exist. A Constraint allows a scheduler to accurately reflect real-world aspects of a project.
In Primavera P6 there are two levels of Constraints: Project Level and Activity Level.
Project Level Constraints
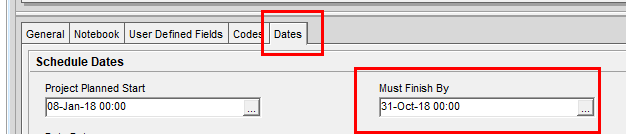
At the project level, you may need to deliver the project by a due date imposed by management or a contract. When a Must Finish By date is applied or changed, there is chance that the project may not be able to complete on time, and adjustment of duration or logic on the critical path activities may be necessary. This due date can be set for the entire project in the Project window of each project by selecting a Must Finish By date.
Activity Level Constraints
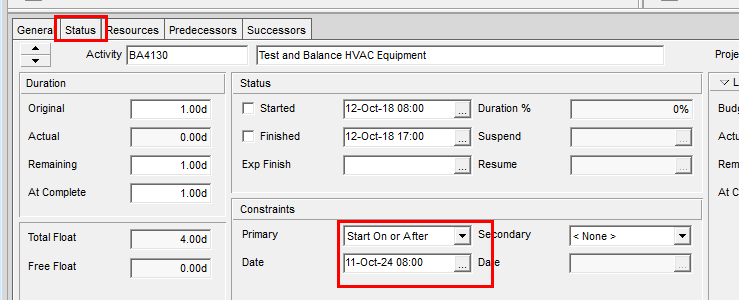
Normally, the start and finish dates of an activity are determined by its relationship to predecessor activities, but by applying a Constraint it can “force” an activity date. Constraints should only be applied if required, and the reason for the Constraint should be documented on the activity - usually by adding an activity note. It is best practice to limit the number of Constraints in a project to 5% of the total activities in that project. Overuse of Constraints can lead to unrealistic schedules.
There are a number of reasons that a Constraint may be necessary on an activity, such as external Constraints imposed by outside factors such as a contractual obligation (i.e. milestone payments based on specific deliverable dates) or when an activity cannot start until a specific condition is met (i.e. waiting on third party approval before proceeding). There may also be internal Constraints, such as management targets or resource/skill limits (i.e. a limit to the number of skilled staff that are available).
There are nine types of Constraints available in P6. Some are soft Constraints, which allow the activity to move forward or backward, and some are hard Constraints, which do not allow the movement of an activity and remove any float on an activity, potentially violating network logic in some cases.
Soft Constraints:
It isn’t immediately obvious which activities are constrained, since you would have to view the Status tab and then individually scroll through every activity to see if it has a Constraint. Below are several different ways for you to easily determine which activities in the project are constrained.
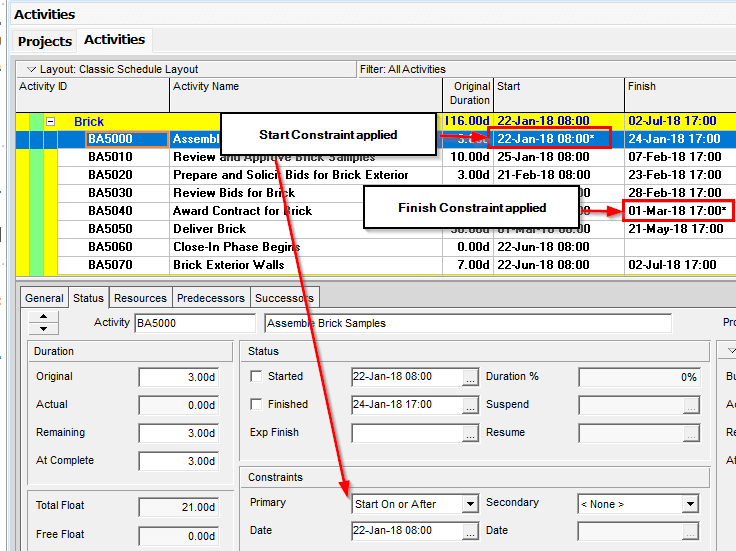
When a Constraint is applied to an activity, an asterisk will show after the date on the Start or Finish date columns in the activity table. A Start Constraint will show an asterisk in the Start date column, while a Finish Constraint will show in the Finish date column.
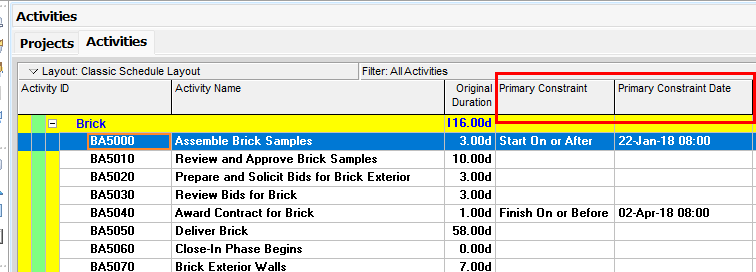
The Primary and Secondary Constraint columns may also be added to the activity table.
Constrained activities can also be viewed in the Schedule Log.
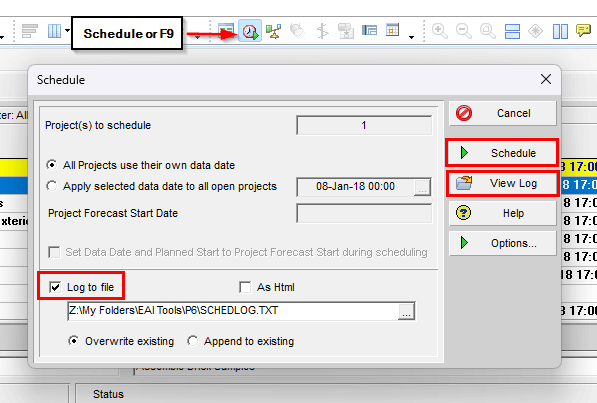
In the schedule log, there is a section that indicates which activities have Constraints.
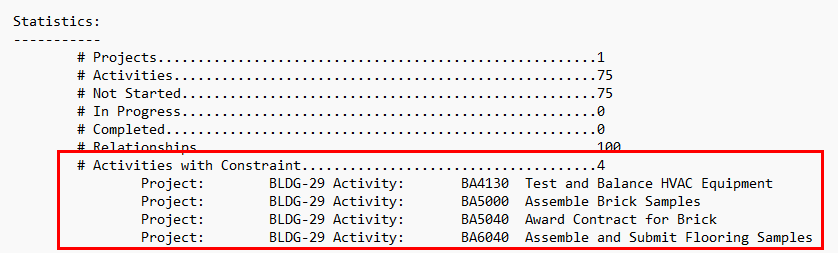
Primavera P6 also has default filters available to filter for constrained activities. If applying both filters, set the activities that match to “Any selected filter”.
There are some considerations that should be taken into account when applying Constraints:
No video selected.
Project Level Constraints
At the project level, you may need to deliver the project by a due date imposed by management or a contract. When a Must Finish By date is applied or changed, there is chance that the project may not be able to complete on time, and adjustment of duration or logic on the critical path activities may be necessary. This due date can be set for the entire project in the Project window of each project by selecting a Must Finish By date.

Activity Level Constraints
Normally, the start and finish dates of an activity are determined by its relationship to predecessor activities, but by applying a Constraint it can “force” an activity date. Constraints should only be applied if required, and the reason for the Constraint should be documented on the activity - usually by adding an activity note. It is best practice to limit the number of Constraints in a project to 5% of the total activities in that project. Overuse of Constraints can lead to unrealistic schedules.
There are a number of reasons that a Constraint may be necessary on an activity, such as external Constraints imposed by outside factors such as a contractual obligation (i.e. milestone payments based on specific deliverable dates) or when an activity cannot start until a specific condition is met (i.e. waiting on third party approval before proceeding). There may also be internal Constraints, such as management targets or resource/skill limits (i.e. a limit to the number of skilled staff that are available).
There are nine types of Constraints available in P6. Some are soft Constraints, which allow the activity to move forward or backward, and some are hard Constraints, which do not allow the movement of an activity and remove any float on an activity, potentially violating network logic in some cases.
Soft Constraints:
- Start On – This forces an activity to start on the Constraint date. It sets the specific date, but allows the the activity to start earlier or later if logic permits within its float.
- Start On or Before – This forces the activity to start no later than the Constraint date.
- Start On or After – This sets the start date of the activity to be equal to or later than the Constraint date.
- Finish On – This is used to force an activity to finish on the Constraint date. It sets the specific date, but allows the activity to finish earlier if logic permits, showing negative float if delayed but preserving network flow.
- Finish On or Before – This forces the activity to be completed by the Constraint date.
- Finish On or After – This forces the earliest date the activity can be completed.
- As Late As Possible – This considers the free float of an activity and forces the activity or milestone to be postponed without affecting the start of the successor activity (depending on the size of the free float).
- Mandatory Start – This forces the early and late start dates of an activity to be the same as the Constraint date, regardless of the schedule calculation logic.
- Mandatory Finish – This forces the early and late finish dates of an activity to be the same as the Constraint date, regardless of the schedule calculation logic.

It isn’t immediately obvious which activities are constrained, since you would have to view the Status tab and then individually scroll through every activity to see if it has a Constraint. Below are several different ways for you to easily determine which activities in the project are constrained.
When a Constraint is applied to an activity, an asterisk will show after the date on the Start or Finish date columns in the activity table. A Start Constraint will show an asterisk in the Start date column, while a Finish Constraint will show in the Finish date column.

The Primary and Secondary Constraint columns may also be added to the activity table.

Constrained activities can also be viewed in the Schedule Log.

In the schedule log, there is a section that indicates which activities have Constraints.

Primavera P6 also has default filters available to filter for constrained activities. If applying both filters, set the activities that match to “Any selected filter”.

There are some considerations that should be taken into account when applying Constraints:
- Scheduling - Always re-schedule after applying a Constraint to see its effect.
- Impact on float - Constraints change float, sometimes creating negative float, which signals a delay.
About the Author
Sue Fermelia - Implementation Specialist
At Emerald Associates, Sue is an Implementation Specialist and has been successful at drawing on her accounting and project management background to consult with our diverse client base. With her friendly demeanor and strong communication skills, she has become a talented Primavera P6 trainer and works very hard to effectively implement Oracle Primavera solutions that cater to each client’s unique organizational needs.